Risk Assessment
for 5 Cancer types

Cancer Guidance?
Call 82684 82684

Protect Yourself from
Cervical Cancer

Download
Karkinos App

Leading Oncology Experts
Guidance for High Risk Population
Digital Oncology Platform
Call the Command Center
Connect with our Command Center for follow up, teleconsult with our doctors.
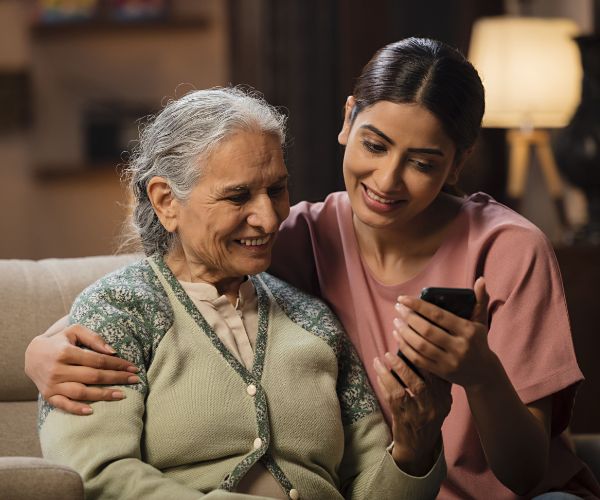

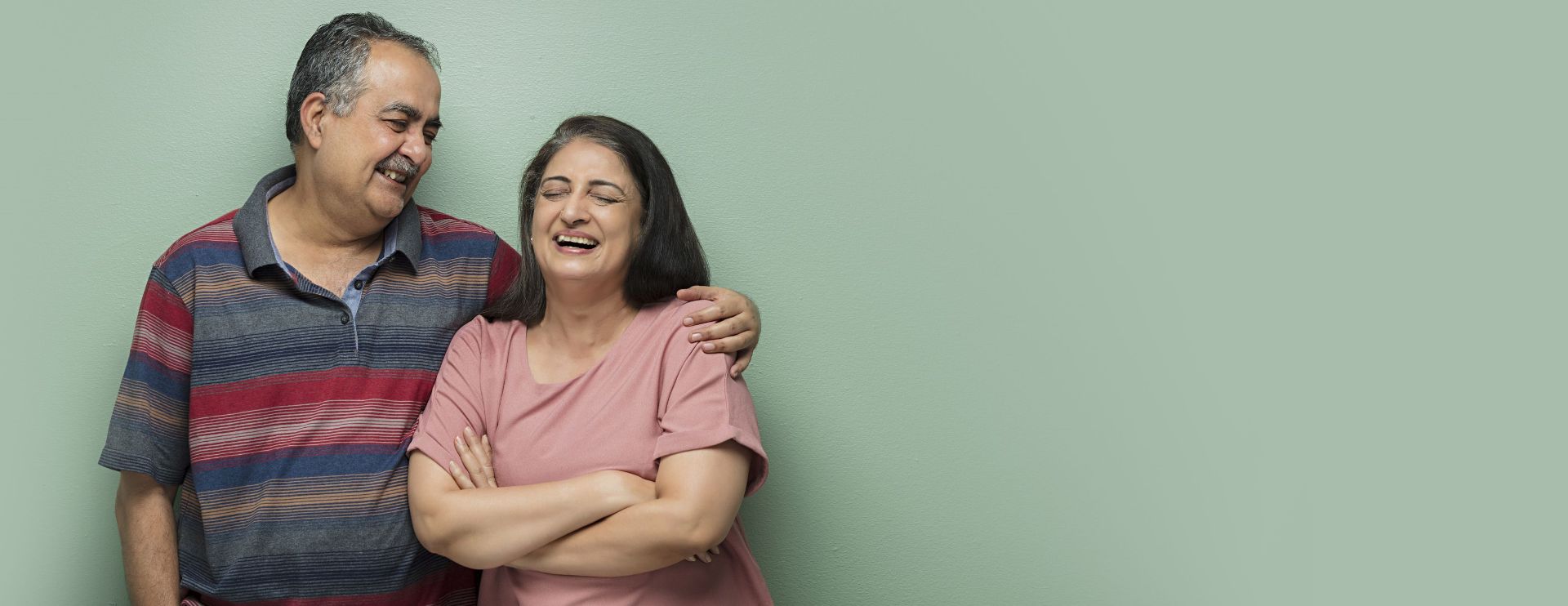
To care for her
Care for your loved ones,
for a healthy & long life.
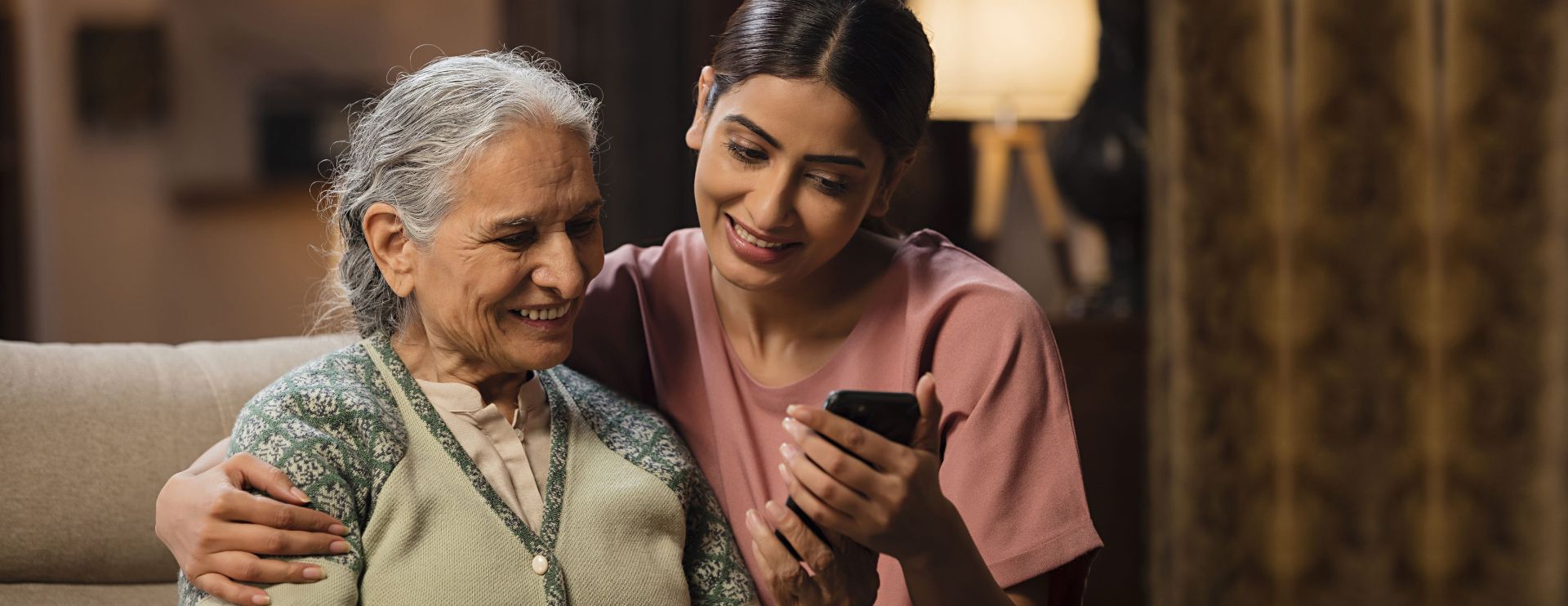


To care for her
Care for your loved ones,
for a healthy & long life.
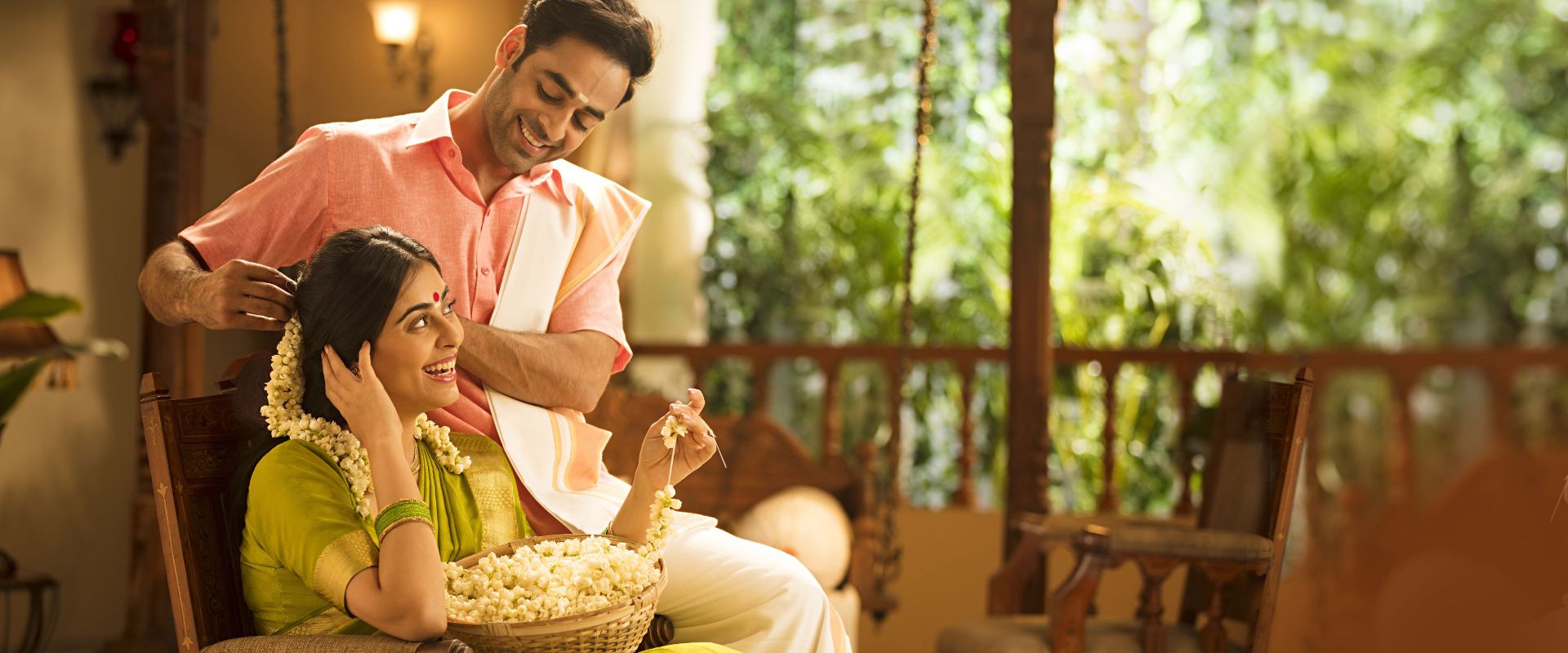
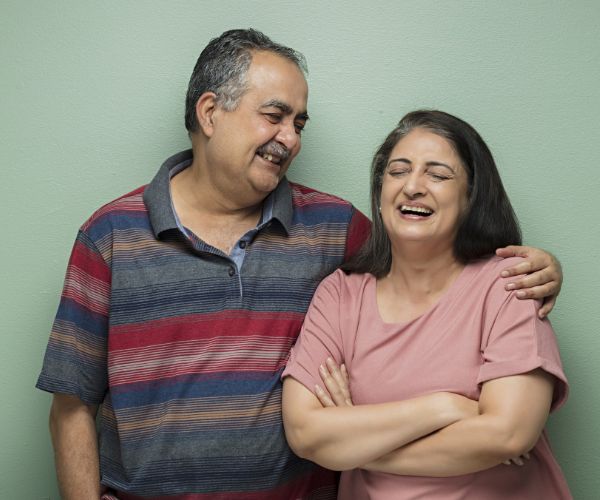


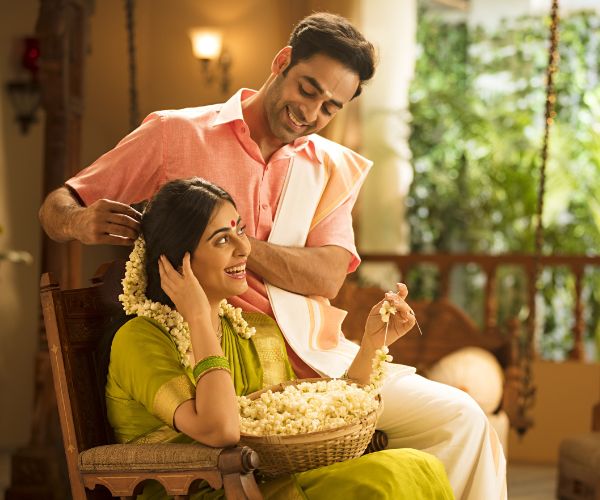
of your loved ones
Regular screening helps in early detection.
Get yourself screened today.
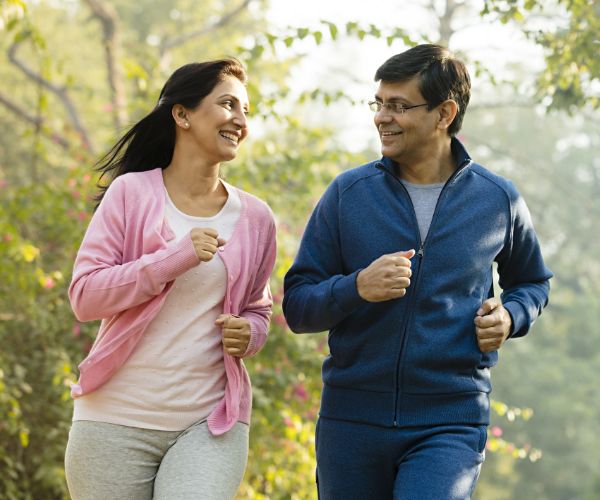


& get yourself screened
regularly
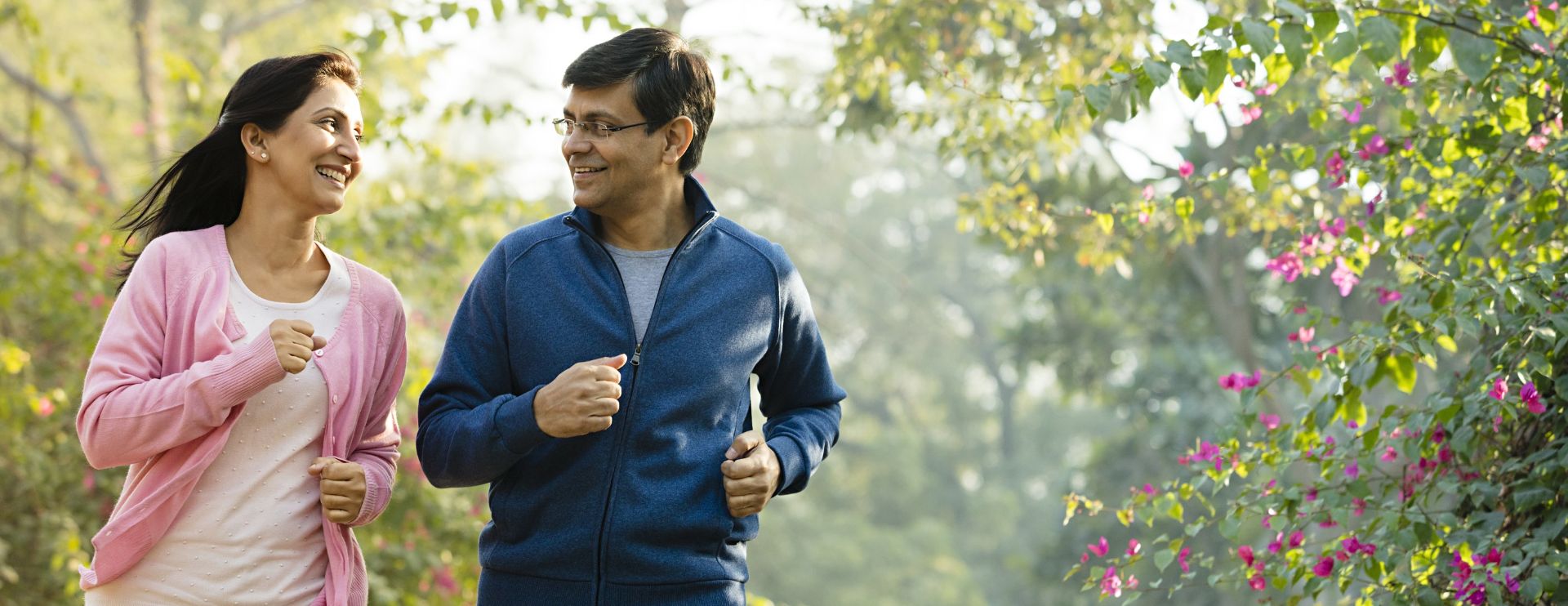

Karkinos is your comprehensive care partner
in your cancer treatment journey

Risk Assessment based
Early Screening

Consult with
the best Oncologists

Experienced
Care Navigator

Near Home
Partner Hospitals

Personalized
Advanced Diagnostics

Mental Health
Support

Community
Support
Nutrition & Lifestyle
Management

Financial Guidance
& Support

Cutting Edge
Cancer Research
Risk Assessment
for 5 Cancer types

Ask us anything,
Cancer.

Upload your
Reports

Download
Karkinos App

K-Vani
Latest News
Thought Leadership, Articles, Whitepapers, Podcasts and much more
- All
- Cancer Expert Talk
- Karkinos in Press & Media
- Leadership
- Let's Talk About Cancer
- Newsroom
- White Paper
- All
- Cancer Expert Talk
- Karkinos in Press & Media
- Leadership
- Let's Talk About Cancer
- Newsroom
- White Paper
- All
- Cancer Expert Talk
- Karkinos in Press & Media
- Leadership
- Let's Talk About Cancer
- Newsroom
- White Paper
- All
- Cancer Expert Talk
- Karkinos in Press & Media
- Leadership
- Let's Talk About Cancer
- Newsroom
- White Paper
Frequently Asked Questions
Cancer is the uncontrolled growth of abnormal cells anywhere in a body. These abnormal cells are termed cancer cells, malignant cells, or tumor cells. Many cancers and the abnormal cells that compose the cancer tissue are further identified by the name of the tissue that the abnormal cells originated from (for example, breast cancer, lung cancer, colon cancer). Cancer is not confined to humans; animals and other living organisms can get cancer. Below is a schematic that shows normal cell division and how when a cell is damaged or altered without repair to its system, the cell usually dies. Also shown is what occurs when such damaged or unrepaired cells do not die and become cancer cells and show uncontrolled division and growth – a mass of cancer cells develop. Frequently, cancer cells can break away from this original mass of cells, travel through the blood and lymph systems, and lodge in other organs where they can again repeat the uncontrolled growth cycle. This process of cancer cells leaving an area and growing in another body area is termed metastatic spread or metastasis. For example, if breast cancer cells spread to a bone, it means that the individual has metastatic breast cancer to bone. This is not the same as “bone cancer,” which would mean the cancer had started in the bone.
There are over 200 types of cancers; most can fit into the following categories according to the research:
- Carcinoma: Cancer that begins in the skin or in tissues that line or cover internal organs.
- Sarcoma: Cancer that begins in bone, cartilage, fat, muscle, blood vessels, or other connective or supportive tissue.
- Leukemia: Cancer that starts in blood-forming tissue such as the bone marrow and causes large numbers of abnormal blood cells to be produced and enter the blood.
- Lymphoma and myeloma: Cancers that begin in the cells of the immune system.
- Central nervous system cancers: Cancers that begin in the tissues of the brain and spinal cord.
How does cancer start?
Your body is made up of many different types of cells. Under normal conditions, cells grow, divide, become old, and die. Then, in most cases, they’re replaced by new cells. But sometimes cells mutate grow out of control, and form a mass, or tumor, instead of dying. Tumors can be benign (noncancerous) or malignant (cancerous). Cancerous tumors can attack and kill your body’s tissues. They can also spread to other parts of the body, causing new tumors to form there. This process is called metastasis and it represents cancer that has advanced to a late stage.
Warning Signal of Cancer:
Remember CAUTION:
C : Change in bowel or bladder habits
A : A wound that does not heal
U : Unusual bleeding or discharge
T : Thickening or lump in the breast or elsewhere
I : Indigestion or difficulty in swallowing
O : Obvious change in a wart or mole
N : Nagging cough or hoarseness of voice
Early Detection of Cancer
• Create awareness about the early warning signs of cancer
• Encourage breast awareness
• Encourage oral self-examination
• Create awareness about symptoms of cervical cancer
• Examine, as a routine, the oral cavity of patients with history of tobacco use
• Offer clinical breast examination/ screening for cervical cancer to any woman over 30 years presenting to health facility.
• Promptly refer any person with a suspicious lesion for accurate diagnosis and treatment
A List of References about Cancer:
1. MOHFW, Govt of India: https://main.mohfw.gov.in/sites/default/files/3651434918nccp4_0.pdf
2. India Against Cancer: http://cancerindia.org.in/faqs/
3. Indian Cancer Society: https://www.indiancancersociety.org/cancer-information/
4. Global Cancer Concern India: https://www.globalcancer.org/faq-on-cancer/
5. National Health Mission: https://nhm.gov.in/index1.php?lang=1&level=3&sublinkid=1122&lid=640
Cancer is the uncontrolled growth of abnormal cells anywhere in a body. These abnormal cells are termed cancer cells, malignant cells, or tumor cells. Many cancers and the abnormal cells that compose the cancer tissue are further identified by the name of the tissue that the abnormal cells originated from (for example, breast cancer, lung cancer, colon cancer). Cancer is not confined to humans; animals and other living organisms can get cancer. Below is a schematic that shows normal cell division and how when a cell is damaged or altered without repair to its system, the cell usually dies. Also shown is what occurs when such damaged or unrepaired cells do not die and become cancer cells and show uncontrolled division and growth – a mass of cancer cells develop. Frequently, cancer cells can break away from this original mass of cells, travel through the blood and lymph systems, and lodge in other organs where they can again repeat the uncontrolled growth cycle. This process of cancer cells leaving an area and growing in another body area is termed metastatic spread or metastasis. For example, if breast cancer cells spread to a bone, it means that the individual has metastatic breast cancer to bone. This is not the same as “bone cancer,” which would mean the cancer had started in the bone.
There are over 200 types of cancers; most can fit into the following categories according to the research:
- Carcinoma: Cancer that begins in the skin or in tissues that line or cover internal organs.
- Sarcoma: Cancer that begins in bone, cartilage, fat, muscle, blood vessels, or other connective or supportive tissue.
- Leukemia: Cancer that starts in blood-forming tissue such as the bone marrow and causes large numbers of abnormal blood cells to be produced and enter the blood.
- Lymphoma and myeloma: Cancers that begin in the cells of the immune system.
- Central nervous system cancers: Cancers that begin in the tissues of the brain and spinal cord.
How does cancer start?
Your body is made up of many different types of cells. Under normal conditions, cells grow, divide, become old, and die. Then, in most cases, they’re replaced by new cells. But sometimes cells mutate grow out of control, and form a mass, or tumor, instead of dying. Tumors can be benign (noncancerous) or malignant (cancerous). Cancerous tumors can attack and kill your body’s tissues. They can also spread to other parts of the body, causing new tumors to form there. This process is called metastasis and it represents cancer that has advanced to a late stage.
Warning Signal of Cancer:
Remember CAUTION:
C : Change in bowel or bladder habits
A : A wound that does not heal
U : Unusual bleeding or discharge
T : Thickening or lump in the breast or elsewhere
I : Indigestion or difficulty in swallowing
O : Obvious change in a wart or mole
N : Nagging cough or hoarseness of voice
Early Detection of Cancer
• Create awareness about the early warning signs of cancer
• Encourage breast awareness
• Encourage oral self-examination
• Create awareness about symptoms of cervical cancer
• Examine, as a routine, the oral cavity of patients with history of tobacco use
• Offer clinical breast examination/ screening for cervical cancer to any woman over 30 years presenting to health facility.
• Promptly refer any person with a suspicious lesion for accurate diagnosis and treatment
A List of References about Cancer:
1. MOHFW, Govt of India: https://main.mohfw.gov.in/sites/default/files/3651434918nccp4_0.pdf
2. India Against Cancer: http://cancerindia.org.in/faqs/
3. Indian Cancer Society: https://www.indiancancersociety.org/cancer-information/
4. Global Cancer Concern India: https://www.globalcancer.org/faq-on-cancer/
5. National Health Mission: https://nhm.gov.in/index1.php?lang=1&level=3&sublinkid=1122&lid=640